Our Services
34,781 views
Contents
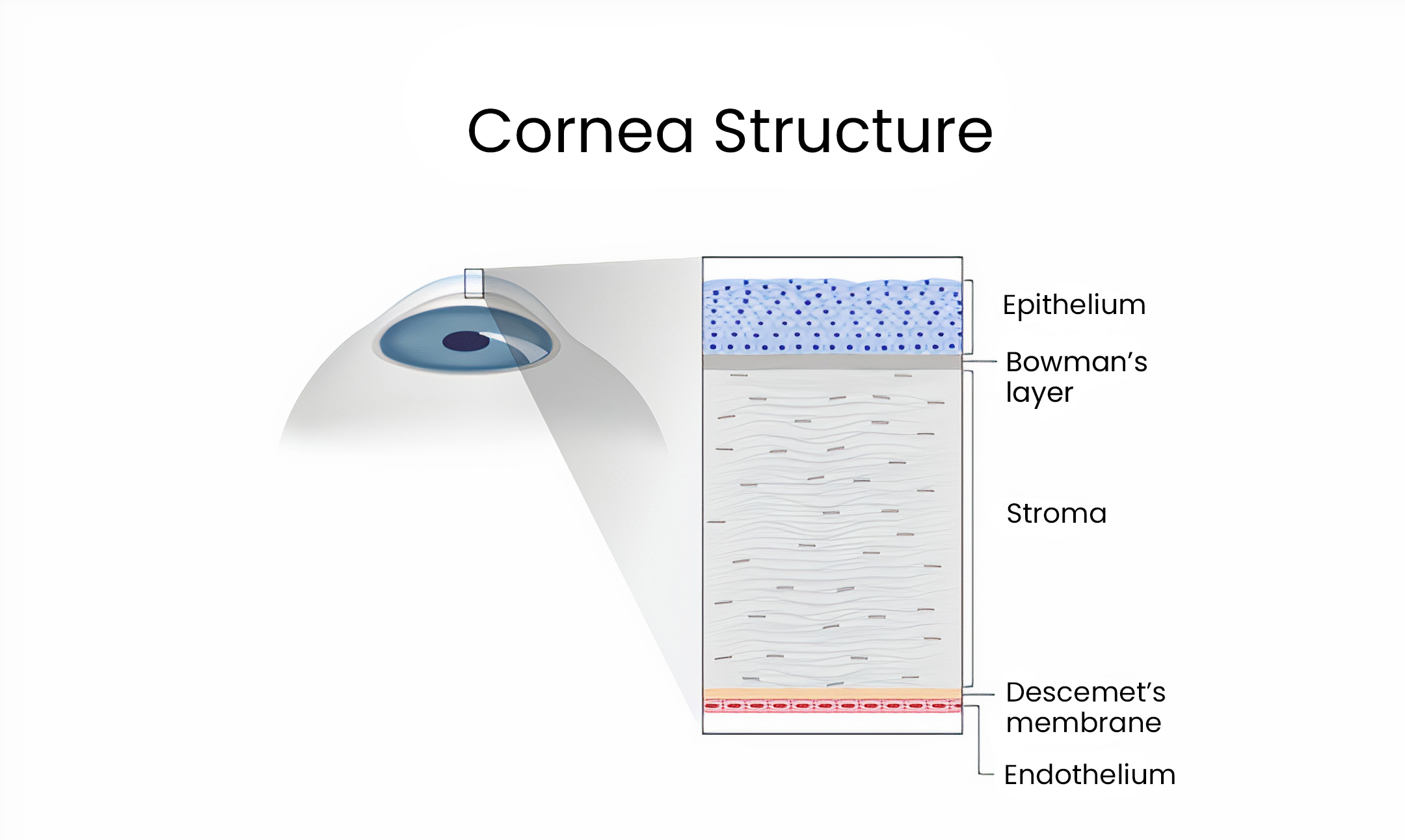
Cornea
Corneal Abnormalities
Causes of corneal abnormalities include:
- Infection
- Keratoconjunctivitis is inflammation of the front of the eye. Complaints that often arise are red eyes, itching, pain, and can be accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity.
- Corneal Infection (Keratitis) happen when a person complain of light intolerance or photophobia. There are several causes of infected cornea, including:
- Viral : Typical picture is well-defined according to the virus that causes it
- Acanthamoeba : caused by wearing contact lenses, sometimes even while swimming. The symptoms you feel will be very painful
- Bacterial : the picture of the infection has a more blurred boundary when compared to the virus, many occur in contact lens wearers with poor hygiene status, sometimes if the infection gets more severe it can cause pus in the eye.
- Fungal : infection in someone who washes their eyes with betel water/breast milk or uses over-the-counter steroid eye drops to treat pink eye. The picture of infection by fungi will be increasingly blurred with a characteristic picture.
- Dystrophy
Dystrophy is an acquired corneal disorder due to genetic inheritance. In one family, there are several family members who have the same disorder. Characteristics that exist is a typical picture with a certain pattern (depending on which layer of the cornea is affected). a person with dystrophic disorder will complain of blurred vision and photophobia / sensitivity to light. Some of the most common dystrophies include:
- ABMD : one of the reasons a person will complain of repeated injuries/erosions (RCE)
- Stromal dystrophy : is a group of non-inflammatory genetic diseases, usually affecting both eyes in the stromal layer of the cornea, which is characterized by a pathognomonic pattern of corneal deposition and morphological changes that can be seen on slit lamp examination
- Granular dystrophy: abnormalities in the stroma with a characteristic appearance such as breadcrumbs (breadcrumbs)
- Avellino dystrophy : a genetic disorder that appears in childhood or adolescence with a combined granular and lattice appearance in the stroma
- Fuchs dystrophy : a disorder in which the number of endothelial cells is insufficient to keep the cornea clear
- Trauma
- Chemical: is an eye emergency and must be treated immediately. The longer the time between trauma and initial treatment, the worse the prognosis
- Blunt: Blunt trauma to the cornea can cause disruption of the endothelial layer which is characterized by a clinical picture of a gray ring on the endothelial layer. Damage can occur up to several years after the traumatic event
- RCE / Mechanical: characterized by eye pain, can not stand to see light, foreign body sensation, and watery eyes that often repeated usually when waking up or when rubbing the eyes
- Ectasia
- Pellucid Marginal Degenerative : It results from asymmetrical thinning of the cornea at the lower edge of the cornea. Patients rarely complain of pain or red eyes, usually marked by decreased visual acuity.
- Keratokonus : This thinning of the cornea should be suspected if a person has a complaint of astigmatism / high vision cylinders that cannot be corrected optimally with glasses. Someone will complain that they have repeatedly gone to opticians but no one can give the right size of glasses.
- Keratecsia/Ectasia post LVC : is a complication after laser vision correction (LASIK, SMILE, PRK) characterized by decreased visual acuity after surgery. This can be prevented by taking into account risk factors and selecting appropriate measures and tools according to each patient's unique condition when consulting before vision correction surgery.
- Pediatric Corneal Opacity
- Pediatric Corneal Opacity is the appearance of the cornea that is not clear in children aged <18 years. Most are caused by genetic disorders, but children should be examined by an ophthalmologist if they experience these complaints
- Corneal Pigmentation
- Band Keratopathy : the appearance of perforated plaques resembling the appearance of swiss cheese that can cross the entire length of the cornea
Our Care Team
Head Of Service
Member of Services
, PhD-1840914967.jpg)
Prof. Dr. Tjahjono D. Gondhowiardjo, SpM(K), PhD
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Dry Eye , SMILE PRO, PhD-1840914967.jpg)
Prof. Dr. Tjahjono D. Gondhowiardjo, SpM(K), PhD
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Dry Eye , SMILE PRO
.jpg)
Prof. Dr. Ni Ketut Niti Susila, SpM(K)
Glaucoma , Cornea , Contact Lens , Comprehensive Ophthalmology , Ocular Infection & Immunology.jpg)
Prof. Dr. Ni Ketut Niti Susila, SpM(K)
Glaucoma , Cornea , Contact Lens , Comprehensive Ophthalmology , Ocular Infection & Immunology
.jpg)
DR. Dr. Made Susiyanti, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Ocular Infection & Immunology.jpg)
DR. Dr. Made Susiyanti, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Ocular Infection & Immunology
.jpg)
DR. Dr. Vidyapati Mangunkusumo, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Contact Lens , SMILE PRO.jpg)
DR. Dr. Vidyapati Mangunkusumo, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Contact Lens , SMILE PRO
.jpg)
Dr. Cokorda Istri Dewiyani Pemayun, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Glaucoma , Cornea , SMILE , Comprehensive Ophthalmology.jpg)
Dr. Cokorda Istri Dewiyani Pemayun, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Glaucoma , Cornea , SMILE , Comprehensive Ophthalmology
-615b40819f.jpg)
Dr. Sharita R. Siregar, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Ocular Inflammation & Immunology , SMILE PRO-615b40819f.jpg)
Dr. Sharita R. Siregar, SpM(K)
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , Ocular Inflammation & Immunology , SMILE PRO

Dr. Cokorda Agung Dalem Pemayun, SpM
Cataract , Glaucoma , Cornea , Comprehensive Ophthalmology
Dr. Cokorda Agung Dalem Pemayun, SpM
Cataract , Glaucoma , Cornea , Comprehensive Ophthalmology

Dr. I Gusti Putu Eka Suryawan Widnyana, M.Biomed, SpM
Cataract , Cornea , Comprehensive Ophthalmology
Dr. I Gusti Putu Eka Suryawan Widnyana, M.Biomed, SpM
Cataract , Cornea , Comprehensive Ophthalmology

Dr. Nyoman Yenny Khristiawati, M.Biomed, SpM, M.H
Cataract , LASIK , Cornea , SMILE , Comprehensive Ophthalmology



 INA
INA_(1).jpg)
.jpg)
-040f44c1d9.jpg)
-90ec36d0dc.jpg)
-bac014abce.jpg)
.jpg)
-d3efc1d442.jpg)




